🔐 The Critical Security Distinction
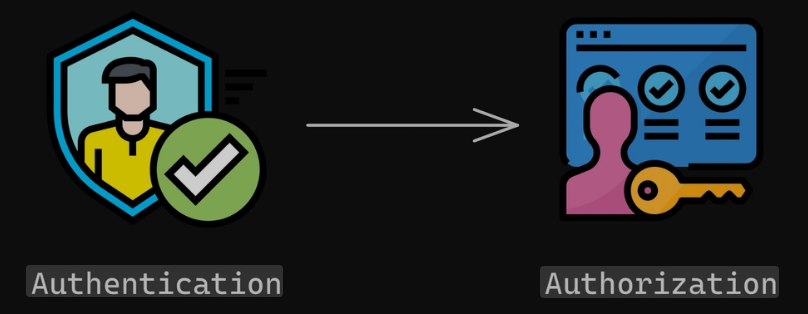
Authentication verifies who you are, while authorization determines what you can do. Understanding this fundamental difference is essential for building secure digital systems in 2025.

Authentication verifies who you are, while authorization determines what you can do. Understanding this fundamental difference is essential for building secure digital systems in 2025.
Purpose: Verify identity
Question: “Who are you?”
Process: Credential validation
Example: Showing your ID at a building entrance
Purpose: Grant permissions
Question: “What can you do?”
Process: Access control enforcement
Example: Having different access levels within the building
The distinction between these concepts has never been more critical. According to recent cybersecurity research, 81% of security incidents are caused by breached credentials, while 75% of security failures through 2025 will result from inadequate management of identities, access, and privileges. The financial impact is substantial, with 51% of organizations suffering financial losses due to identity-related breaches.
The adoption of robust authentication has accelerated dramatically. The global MFA market is projected to reach $49.7 billion by 2032, growing from $14.4 billion in 2023. This growth reflects the increasing recognition that password-only authentication is insufficient against modern threats.
Organizations using multiple authentication factors experience 99.9% fewer account compromises than those relying solely on passwords. Microsoft research shows that 2FA has successfully blocked 99.9% of automated attacks.
The shift toward passwordless authentication is accelerating in 2025. The global passwordless authentication market is expected to reach $22 billion this year, with projections approaching $90 billion in the next decade.
Biometric technology is experiencing a renaissance in 2025, moving beyond traditional fingerprint scanning to more sophisticated methods. In 2025, multimodal biometric systems that combine two or more types of biometric data are gaining prominence, offering enhanced security that’s harder to spoof.
Modern organizations are increasingly choosing between Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) and Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC) models based on their specific security requirements.
| Aspect | RBAC | ABAC |
|---|---|---|
| Approach | Permissions assigned to predefined roles | Dynamic evaluation based on user, resource, and environmental attributes |
| Complexity | Simple to implement and manage | Requires more effort but offers greater flexibility |
| Best Use Case | Structured environments with static roles | Complex environments requiring context-aware decisions |
| Scalability | Scales well with organizational growth | Highly flexible for diverse scenarios |
The global RBAC market is expected to grow to $15.3 billion by 2025, driven by increased adoption in both SMEs and large enterprises. However, organizations are moving beyond traditional RBAC and ABAC to implement Policy-Based Access Control (PBAC), which provides more granular and dynamic access management.
Zero Trust security has become a cornerstone of modern authorization strategies. 84% of organizations are actively pursuing Zero Trust for cloud security, with 81% having fully or partially implemented a Zero Trust model.
Zero Trust frameworks ensure that every access request is continuously verified regardless of user location or device. This approach treats identity as the new perimeter, requiring authentication and authorization for every transaction, even within the corporate network.
The evolution from OAuth 2.0 to OAuth 2.1 represents a significant security improvement. OAuth 2.1 isn’t a radical rewrite but rather deprecates risky flows and formalizes best practices. This update addresses critical vulnerabilities that have emerged over OAuth 2.0’s decade-plus lifespan.
Key OAuth 2.1 Security Improvements:
Organizations often must choose between JWT and SAML tokens based on their specific requirements and existing infrastructure.
| Characteristic | JWT | SAML |
|---|---|---|
| Format | JSON-based, compact and lightweight | XML-based, more verbose and complex |
| Size & Speed | Smaller size, faster transmission | Larger tokens, may slow exchanges but more robust |
| Use Case | APIs, web services, mobile apps | Enterprise SSO, inter-organizational authentication |
| Security | Token-based security with scopes | Strong security with signed XML assertions |
The cybersecurity landscape in 2025 has seen significant security incidents that underscore the importance of robust authentication and authorization systems.
Recent breaches have highlighted common authentication vulnerabilities that organizations must address:
AI-powered Identity Threat Detection and Response (ITDR) is emerging as a critical new layer in the modern identity stack. Organizations are leveraging machine learning to establish normal access patterns and flag deviations that might indicate compromised credentials.
AI-Driven Authentication: machine learning algorithms establish normal access patterns and flag deviations that might indicate compromised credentials. AI-driven authorization decisions will become standard across enterprise applications, with systems automatically adjusting permissions based on real-time risk assessments.
Behavioral Biometrics: analysis of unique user interaction patterns for continuous authentication throughout a session. This passive method works in the background, verifying identity without interruption.
Quantum-Resistant Cryptography: organizations are preparing for post-quantum authentication methods to future-proof security against advances in quantum computing.
Decentralized Identity Models: self-sovereign identity (SSI) is gaining momentum, allowing individuals to own and control their digital identities without relying on central authorities. Blockchain technology increasingly facilitates this model with secure, immutable records.
Q: What’s the main difference between authentication and authorization?
Authentication verifies who you are, while authorization determines what you’re allowed to do. Authentication always happens first, then authorization grants or denies specific permissions based on that verified identity.
Q: Is multi-factor authentication really necessary in 2025?
Yes. With 81% of security incidents caused by breached credentials and organizations using MFA experiencing 99.9% fewer account compromises, MFA is essential. The global MFA market reaching $49.7 billion by 2032 reflects its critical role.
Q: Should I use OAuth 2.0 or OAuth 2.1 for new projects?
Use OAuth 2.1. It eliminates insecure flows like implicit grants, mandates PKCE for all clients, and enforces security best practices by default, offering clearer guidelines and stronger protection.
Q: When should I choose RBAC vs ABAC for authorization?
RBAC suits structured environments with clearly defined roles and static responsibilities. ABAC fits complex contexts needing dynamic, attributebased decisions. Many organizations adopt a hybrid approach to leverage both models.
Check us out for more cybersecurity insights at SoftwareStudyLab.com
