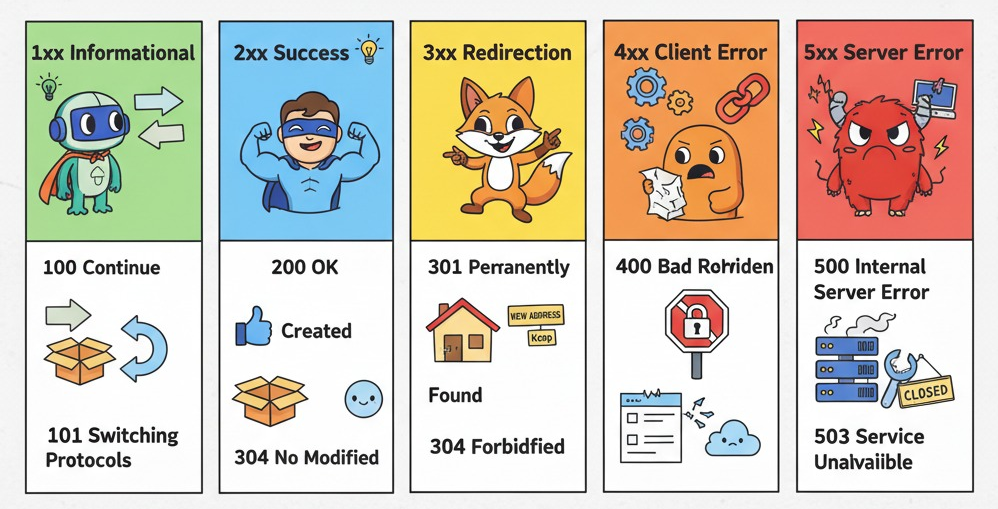
HTTP Status Codes Cheat Sheet: 200, 201, 301, 404, 500
HTTP status codes are the universal language servers use to communicate the outcome of client requests. Mastering key codes like 200, 201, 301, 404, and 500 is essential for developers, SEO professionals, and webmasters to optimize websites, enhance user experience, and maintain strong search engine rankings.
Quick Reference Cheat Sheet
200 OK
Request successful, content returned.
201 Created
New resource successfully created.
301 Moved Permanently
Permanent URL redirection, SEO value preserved.
404 Not Found
Requested page/resource not found.
500 Internal Server Error
Generic server error, request failed.
Understanding HTTP Status Codes
What Are HTTP Status Codes?
HTTP status codes are three-digit responses sent by servers to clients (browsers or APIs) indicating the result of an HTTP request. They help browsers, users, and search engines understand if content was successfully served, redirected, or if an error occurred. Proper usage improves communication and site performance.
The Five Categories of Status Codes
- 1xx – Informational: Server is processing the request.
- 2xx – Success: Request was successfully completed (e.g., 200 OK, 201 Created).
- 3xx – Redirection: Client needs to perform further action (e.g., 301 Moved Permanently).
- 4xx – Client Errors: Issues with the request or resource (e.g., 404 Not Found).
- 5xx – Server Errors: Server failed to fulfill the request (e.g., 500 Internal Server Error).
Key HTTP Status Codes You Must Know
200 OK
The most common success code indicating the request was successful and the content is served as expected. This status ensures users and clients that everything worked perfectly.
201 Created
This status indicates that a new resource was successfully created on the server, useful in APIs responding to POST requests that add new data.
301 Moved Permanently
Use 301 when a resource has been permanently moved to a new URL. It instructs search engines to transfer SEO value to the new location, preserving rankings.
404 Not Found
This indicates the requested resource cannot be found. Frequent 404 errors frustrate users and can degrade SEO if not managed properly.
500 Internal Server Error
A generic server error signaling that the server failed to process the request due to an internal issue. Prompt troubleshooting is necessary to restore functionality.
Why HTTP Status Codes Matter for SEO & User Experience
HTTP status codes provide critical signals to search engines and users. How search engines treat your site and how users interact with it can hinge on these codes. Proper implementation influences rankings, crawl efficiency, and visitor satisfaction.
SEO Impact
- 301 redirects retain nearly all link equity, crucial during site migrations.
- 404 errors alert search engines to missing pages, which can hurt rankings if excessive.
- 5xx server errors warn of instability and can cause search engines to reduce crawl frequency or deindex pages.
User Experience
Users expect smooth browsing; encountering error pages or failed server responses reduces trust and increases bounce rates. Clear and correct status codes help maintain a seamless experience.
Best Practices for Developers & SEO Specialists
For Developers
- Always send the appropriate status code to clearly reflect the request outcome.
- Use 201 Created for successful resource creation APIs; avoid generic success codes overuse.
- Implement robust handling for client and server errors to facilitate faster debugging and better client feedback.
- Leverage caching codes (like 304 Not Modified) for improved site responsiveness.
- Continuously monitor server logs for abnormal status code patterns indicating issues.
For SEO Specialists
- Use permanent redirects (301) rather than temporary ones (302) for URL changes to preserve SEO.
- Regularly identify and fix or redirect broken links causing 404 errors.
- Minimize the occurrence of 5xx errors by collaborating with developers to ensure backend stability.
- Employ monitoring tools (e.g., Google Search Console) to track and act on status code issues.
Summary & Key Takeaways
HTTP status codes are foundational for web communication, affecting technical performance, SEO rankings, and user satisfaction. Understanding and correctly implementing key codes like 200, 201, 301, 404, and 500 ensures reliable web experiences and effective search engine indexing. Regular monitoring is essential to promptly identify and resolve issues that may harm traffic or reputation.
With modern web applications becoming increasingly complex, HTTP status codes help maintain smooth, reliable operations. Leveraging them effectively supports better content delivery, faster troubleshooting, and stronger SEO performance, providing a competitive advantage in both user experience and search visibility.
Incorporating comprehensive status code handling in APIs and websites also aids in scalability and future-proofing your web infrastructure.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What does HTTP status code 200 mean?
The 200 code means the server successfully processed the request and returned the requested content.
2. How does a 301 redirect affect SEO?
A 301 redirect permanently moves a URL and transfers almost all SEO value from the old address to the new one, preserving search rankings.
3. Why should I avoid too many 404 errors?
Frequent 404 errors frustrate users and harm SEO by signaling broken or missing content, reducing your site’s authority and traffic.
4. What is the best way to handle 500 errors?
Investigate and fix server-side issues causing 500 errors immediately to maintain site stability, prevent user disruption, and safeguard SEO.
Check us out for more at SoftwareStudyLab.com
